How to Maintain Commercial Gas Hoses for Ovens, Fryers & Ranges: Expert Tips
Gas hoses play a pivotal role in the operation of commercial kitchens, serving as the lifelines that deliver propane or natural gas to essential cooking equipment such as ranges, griddles, ovens, and deep fryers. Without reliable hoses, appliances cannot function safely or efficiently, putting kitchen staff and diners at risk. In bustling restaurant environments, gas hoses must withstand constant movement, exposure to heat, and the rigors of daily cleaning routines. Choosing the right hose type and maintaining it properly can prevent dangerous leaks, costly downtime, and regulatory violations. This guide explores the various hose options available, highlights key safety features, outlines common issues and troubleshooting techniques, and offers practical installation, handling, and maintenance tips.
Types of Commercial Gas Hoses
Commercial gas hoses vary by material, design, temperature rating, and connection style. Selecting the optimal hose ensures compatibility with specific appliances and kitchen workflows.
1. Standard stainless steel braided hoses
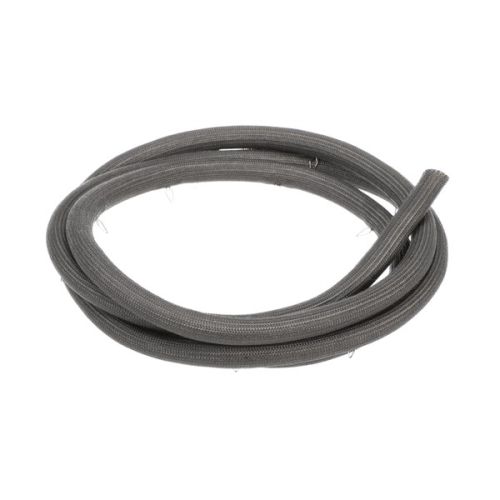
Constructed with an inner rubber or polymer tube wrapped in a stainless steel braid.
-
Advantages: Excellent durability against abrasion and punctures. Flexible for minor appliance relocations. Corrosion-resistant braid prevents rust in high-humidity kitchens.
-
Limitations: It can be heavier than unbraided options. More expensive upfront.
-
Applications: Ideal for ovens, ranges, and fryers where moderate flexibility is needed.
2. Quick-disconnect hoses
Design is fitted with spring-loaded couplings for rapid attachment and detachment.
-
Advantages: Emergency shut-off capability when pulled apart. Speeds up appliance swap-outs for cleaning or maintenance.
-
Considerations: Must be certified for gas use; improper models can leak. Inspect coupling seals regularly.
-
Use cases: Mobile cooking stations, banquet carts, or equipment requiring frequent repositioning.
3. High-temperature resistant hose
The materials can be silicone, Teflon, or specialty polymers that are rated at 400°F (204°C) or higher.
-
Benefits: Maintains integrity near hot ovens, griddles, and broilers. Reduces the risk of hose softening or failure under radiant heat.
-
Drawbacks: Typically stiffer, limiting movement. Higher cost due to specialty compounds.
-
Best For: Lines routed close to heat-generating appliances, such as salamanders or charbroilers.
4. Flexible vs. rigid options
Flexible hoses are bendable without fittings to accommodate minor equipment shifts. Easier installation in confined spaces.
-
Rigid pipe with flexible pigtails: Rigid black iron or steel delivers gas through fixed runs. Flexible pigtails (small braided hoses) connect the final appliance. Offers stability for heavy appliances but allows minimal movement at the connection.
-
Selection Criteria: Evaluate kitchen layout, frequency of equipment moves, and code requirements. Flexible hoses excel in dynamic environments, while rigid runs are preferred for stationary installations.
Key Safety Features of Gas Hoses
Safety features built into modern gas hoses minimise accident risk and ensure compliance with industry standards.
-
Restraining cables: Often called safety cables, these steel wires run alongside braided hoses to catch the hose if it detaches or ruptures. In the event of a sudden break, the cable prevents the hose from whipping around, reducing the likelihood of injury or equipment damage.
-
Quick-disconnect fittings for emergencies: Engineered to separate under excessive force, these fittings automatically stop gas flow when pulled apart. They are critical in kitchens with mobile appliances, providing an additional layer of emergency shut-off beyond the manual valve.
Compliance with industry standards
-
ANSI (American National Standards Institute)
-
CSA (Canadian Standards Association)
-
UL (Underwriters Laboratories)
Hoses and fittings should bear certification marks indicating they meet rigorous testing for pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure. Always verify hose labels and documentation before installation.
Additional safety elements
-
Integrated shut-off valves: Some hoses include built-in valves that activate if internal pressure spikes.
-
Colour-coding: Yellow jackets or bands differentiate gas hoses from water or electrical conduits, preventing misidentification.
-
Protective sleeves: Heat-resistant covers shield hoses from radiant heat and cleaning chemicals.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting Commercial Gas Hoses
Even top-quality hoses can encounter problems. Early detection and prompt action ensure kitchen operations remain safe and uninterrupted.
Hose kinking or twisting
-
Cause: Sharp bends or improper routing, often at the appliance connection.
-
Symptoms: Restricted gas flow, uneven flame patterns, or burner sputtering.
-
Solution: Relocate hoses to maintain gentle curves. Use hose supports or clips to guide proper alignment.
Loose connections are causing gas leaks
-
Detection: Smell of sulfur-like “rotten egg” odor (added as a safety measure) or a soap-water bubble test at fittings.
-
Fixes: Tighten connections with approved wrenches; avoid over-torquing. Replace worn ferrules or gaskets for compression fittings. Retest after tightening.
Signs a gas hose needs immediate replacement
-
Visible cracks or cuts: Any damage to the inner tube or outer braid.
-
Bulging or Soft Spots: Indicates internal breakdown of hose materials.
-
Age beyond manufacturer’s Lifespan: Generally 3–5 years; check product guidelines.
-
Persistent leaks: Even after tightening, it suggests internal failure.
Odorization loss
-
Risk: Undetected leaks if mercaptan (odorant) dissipates.
-
Mitigation: Periodic concentration checks by gas suppliers; ensure proper ventilation to preserve odorants.
Commercial Gas Hoses Installation & Handling Tips
Proper installation and handling extend hose life and enhance kitchen safety.
Correct positioning to avoid strain
-
Route hoses away from high-traffic paths to prevent snagging.
-
Avoid running hoses across hot surfaces; maintain recommended clearance distances.
-
Use brackets or clips to secure hoses, preventing downward sag.
Professional installation guidelines
-
Permits & inspections: Obtain local authority approval before installation.
-
Certified technicians: Use licensed plumbers or gas fitters familiar with commercial kitchen codes.
-
Pressure testing: After installation, leak-test at operating pressure with a gauge and soap solution.
Handling precautions
-
Never drag hoses across sharp edges or abrasive floors.
-
Avoid kinks formed by wrapping hoses too tightly on carts or reels.
-
Keep hoses clear of grease traps and areas of heavy foot traffic.
Gas Interlock Systems: The Ultimate Safety for Busy Commercial Kitchens
Maintenance Tips for Commercial Gas Hoses
Regular maintenance is critical to detect wear early and prevent unexpected failures.
|
Section |
Details |
|
Regular Inspection Routines |
|
|
Cleaning Best Practices in Greasy Environments |
|
|
When and How to Replace Hoses |
|
|
Checking Connections After Moving Equipment |
|
Investing in high-quality gas hoses, installing them correctly, and adhering to rigorous maintenance routines are foundational steps in safeguarding commercial kitchens. Emphasizing safety features, restraining cables, emergency disconnects, and regulatory compliance further reduces risk. Routine inspections, professional installations, and prompt replacement of compromised hoses keep service uninterrupted and protect staff safety. Ultimately, diligent gas hose management underscores a kitchen’s commitment to operational excellence and risk mitigation. PartsFe UK offers a wide range of OEM and compatible parts for commercial kitchens, including dishwasher parts, fryer parts, griddle & grill parts, ice machine parts, oven parts, and plumbing parts. with fast UK-wide shipping and excellent customer support.
FAQs
How often should commercial gas hoses be replaced, even if no damage is visible?
Most manufacturers recommend replacing commercial gas hoses every 5–7 years, even if they appear intact, as material fatigue can lead to hidden risks.
Can I use a residential gas hose in a commercial kitchen setup?
No. Commercial gas hoses are specifically designed for high-demand, high-heat, and frequent-movement environments. Residential hoses lack the durability and safety certifications required in professional kitchens.